Itching
Itching describes the sensation of skin irritation that can occur on one part of the body or in several different areas at a time. Itching is not health condition or disease in itself, but is very often a symptom of some underlying health condition. Itching or Pruritus creates the urge to scratch and may be accompanied by a rash, blisters, or bumps on the skin. Itching without any skin abnormalities and those that are more generalized are often difficult to diagnose and treat.
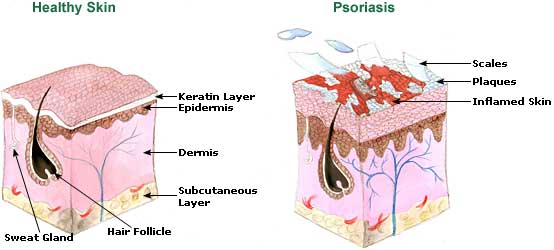
Scratching can increase the intensity of an itch and can lead to further complications such as neurodermatitis, permanent skin damage, scarring, and other bacterial skin infections.
Symptoms of Itching
Itching can be localized, affecting only small areas of skin such as on the arms or legs, back or face. Generalized itching involves the whole body feeling itchy for no apparent reason. Spots, blisters, rashes, and red skin may accompany itchy skin. Other symptoms include dry skin, cracked skin, and a leathery texture of the skin (due to constant scratching).
In some cases, itchiness can get worse at night. Itchy skin can often last for long periods of time and cause anxiety and stress. In case itchy skin does not clear up with self-care and home remedies, visit your dermatologist for a proper diagnosis and treatment.
You should also visit your doctor if itching is accompanied by any of the following symptoms:
- Itching lasts for more than two weeks
- It prevents you from sleeping and the discomfort is severe
- There is no apparent cause for the itching
- Itching has spread all over your body
- Fatigue and weakness
- Loss of appetite
- Weight loss
- Fever
- Redness of skin
- Change in frequency of urination and bowel movements
During the consultation with your doctor or dermatologist you will be asked a number of questions in order to determine the cause of the itching. Some of these questions are:
- How long has the itching lasted?
- Does the itching come and go or is it constant?
- Has the itching spread?
- Have you had this kind of itching before?
- Have you come in contact with an allergen, insect, new product that may be causing the itching?
- Do you have any food allergies?
- Have you been around any animals?
- What other symptoms do you have?
- Are you on any other medication?
In addition to these questions you may be required to undergo a blood test, a skin biopsy or even an x-ray to determine the proper treatment for the itching.
Causes of Itching
Depending on whether the itching is generalized or localized there are several causes. These include:
- Aging
- Contact dermatitis (caused by exposure to poison ivy)
- Allergies to irritants such as chemicals, wool, and soap
- Dry skin
- Insect bites
- Skin parasites such as lice or worms
- Hives
- Skin conditions such as psoriasis
- Exposure to the sun
- Skin infections
- Chickenpox or measles
- Anemia
- Kidney failure
- Problems with the liver (Jaundice)
- Pregnancy
- Reaction to certain medications
- Stress and anxiety
- Metabolic disorders
- Endocrine disorders such as hyperthyroidism
- Cancer
- Cholestasis (problem with the bile flow in the body)
- Fungal infections
- Swimmers itch
- Conditions that affect the nerves such as shingles, diabetes and multiple sclerosis
Remedies for Itching
Home remedies for itchy skin can help relieve symptoms of discomfort and pain without the side effects associated with oral or topical medications.
One of the easiest ways to relieve itching is by using cold water in the form of a bath or shower or a cold compress on the skin. The sensations of cold and itchiness travel along the same neural pathways in the body. Using cold water on the skin can thus reduce the feeling of itchiness. You could either pour cool running water on the affected areas or apply an ice pack for quick relief against itching. Having hot water baths or showers should be avoided when suffering from itchy skin.
Simple ways for itchy skin relief include wearing loose cotton clothes especially to bed, applying a moisturizer or skin lotion to the skin to keep it hydrated, and avoid excess heat and humidity that causes sweating and aggravates itchiness.
Keep in mind that while many of these home remedies are known to help relieve itching, not all of these have been tested scientifically and in some cases, results may vary greatly. Home remedies to relieve itching include:
- Making a paste of sandalwood or using sandalwood oil on the itchy areas of skin to cool the skin and offer some relief. Similarly the oil of neem leaves can provide the same benefits against itchy and dry skin. Neem powder had orally also prevents skin infections that may result in itching.
- Drink a glass of aloe-vera juice first thing in the morning to keep the skin moisturized and heal any skin condition.
- An effective natural treatment for itchy skin is to mix equal quantities of linseed oil and lemon juice and apply this lotion to the skin to cure itchiness.
- Home remedies to stop itching because of dry skin include massaging fresh milk cream on the skin. The cream acts as a natural moisturizer and prevents dry skin when used consistently.
- Apply cream made with chamomile or calendula directly on the affected areas. These ingredients have anti-inflammatory properties that can reduce swelling of the skin, and rashes and bumps and aid the healing process.
- Herbal therapists suggest using the herb Jewelweed as an itch relief home remedy. Jewelweed is a wildflower that can be boiled in water and applied to the skin. Studies show that jewelweed is almost as effective as medical skin creams using hydrocortisone that are used to treat itching.
- Aromatherapy solutions for itchy skin suggest the use of essential oils such as lavender, rosemary or chamomile to soothe and relax inflamed skin. Add a few drops of any of these essential oils to your bath to enjoy their benefits. Alternatively you can dilute them with a neutral carrier oil and apply it to the affected areas of the skin for instant relief.
- Soaking in a bath of lukewarm water with oatmeal or cornstarch added can help reduce itching and swelling of the skin. A few drops of peppermint oil to the bath water can soothe the skin and reduce pain while apple cider vinegar added to the water is another popular itchy skin home remedy.
Diet for Itching
There is a distinct possibility that there may be a correlation between your diet and the symptoms of itchiness. Food allergies can cause rashes and inflammation of the skin that lead to itching. Altering your diet to reduce itching is the best option once you know what foods trigger the itching symptoms.
Foods that are high in proteins can cause allergic reactions in the body. These include nuts, milk, eggs, shellfish, and soy. Some people react to raw nuts, vegetables and fruits such as parsley, pears, apples, hazelnuts, bananas and melons. This is referred to as a pollen-food allergy syndrome and it can cause itchiness around your mouth and throat. This happens because your immune system confuses the proteins in these types of foods as a type of pollen and an allergic reaction is triggered. Cooking the food before you eat it can reduce the symptoms of this syndrome. The reaction to the food items is localized and rarely leads to a medical emergency.
Contact dermatitis can cause red raised patches of skin and severe itching. This happens when a particular food comes in direct contact with your skin. Tomatoes, peanut butter, and kiwis have been known to cause such reactions among certain subjects. If you happen to touch foods that cause this allergy, immediately wash the skin with soap and water and apply a cream that contains hydrocortisone before the itching can start.
Suggestions for Itching
Scratching can cause severe damage to the skin. The cycle of itching and scratching is very difficult to break. To avoid scratching keep your nails as short as possible and file them down so that the jagged edges dont further aggravate the skin. Wear gloves when you sleep to prevent scratching at night. Try and keep your skin covered with clothing at most times, as this will offer some protection if you unwittingly scratch at the skin. Pinching or rubbing the skin instead of scratching is another option. Using a high quality moisturizing cream can also prevent scratching as this soothes the skin and relieves itching. Wear clothes made out of smooth breathable fabrics and use a mild detergent to wash. Avoid exposing your skin to any substances that could cause an allergic reaction such as metals, perfume, and beauty products.
References
- Reuter J, Jocher A, Stump J, Grossjohann B, Franke G, Schempp CM. Investigation of the anti-inflammatory potential of Aloe vera gel (97.5%) in the ultraviolet erythema test. Skin Pharmacol Physiol. 2008;21(2):106-10. doi: 10.1159/000114871. Epub 2008 Feb 5. PubMed PMID: 18253066.
- Bhaskaran N, Shukla S, Srivastava JK, Gupta S. Chamomile: an anti-inflammatory agent inhibits inducible nitric oxide synthase expression by blocking RelA/p65 activity. Int J Mol Med. 2010 Dec;26(6):935-40. PubMed PMID: 21042790; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC2982259.
- Lipton R.A. Comparison of jewelweed and steroid in the treatment of poison ivy contact dermatitis. Ann Allergy. 1958;16:52667.
- Home remedies for itching from sun poisoning: My husband has severe itching which doctors say is from sun poisoning. Nothing helps. He was prescribed a malaria drug and several creams. Any ideas?
Sunburn is from over-exposure to the harmful ultraviolet rays of the sun. The skin damage is... - Advice for flea bites: I have like 200 flea bites on my legs. At least that is what I was told they were. What is the best remedy to cure the bites and to get rid of the itching?
Do you have a pet at home? Please maintain them with utmost care. Check out these for relief... - Suggestions to cure itching: My dog's scratches and his skin is raw looking(pink) what can I do to help relieve the itching.
The most common cause of scratching in pets is mites. Try these natural easy-to-do remedies:... - Cures for anal itch: anal itching how to stop it
Cure To get anal itching relief first an anal itch cure should be prescribed. Itching in the... - Advice for anal itching: After every 4 to 5 months for last 2 years I am getting itching at the anal part and starts paining (only at the beginning) while passing stool. I am 45 y.old. After homeopathic consult it cure. Kindly advise to stop completely
many times medicated vasoline with some quinine mixed.Applied a couple times a day will cure it. - Natural Cures for Insect Bite Itch: How to make a make insect bite quit itching
HI, I get shingles which itch like crazy, i found o wonderful product which cost me two dollars... - Quick relief for extreme itching and poison ivy: how can i get rid or extreme itching and poison ivy? I need IMMEDIATE help. Thank you.
Rubbing the rind of citrus fruits like lemon is seen to be effective. Dabbing the area with corn... - Remedy for itchy skin from bug bites: Itchy skin from bug bites, I have used benadryl, baking soda, you name it it will not stop itching/ What can I use?
Plantain Salve. It works like magic.Spread a little on instant relief. You might have to get...